Anderson and Krathwohl’s Taxonomy
Anderson and Krathwohl’s Taxonomy
Before
starting discussion on new taxonomy, let us have a look at original Bloom’s
Taxonomy.
In Bloom’s taxonomy, there were 6 categories under cognitive domain
i.e.
Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
Except
Application, all other 5 main categories were further divided into
subcategories.
It was a hierarchical structure where categories were arranged
from
simple to complex and concrete to abstract. It was assumed that attainment
of one category is a
prerequisite for next category
KNOWLEDGE Science Teaching-Learning
·
Knowledge of specifics
·
Knowledge of terminology
·
Knowledge of specific facts
·
Knowledge of ways and means of dealing with
specifics
·
Knowledge of conventions
·
Knowledge of trends and sequences
·
Knowledge of classifications and categories
·
Knowledge of criteria
·
Knowledge of methodology
·
Knowledge of universals and abstractions in a field
·
Knowledge of principles and generalizations
·
Knowledge of theories and structures
COMPREHENSION
1. Translation
2. Interpretation
3. Extrapolation
APPLICATION
ANALYSIS
·
Analysis of elements
·
Analysis of relationships
·
Analysis of organizational principles
SYNTHESIS
1. Production
of a unique communication
2. Production of a plan, or proposed set of operations
3. Derivation
of a set of abstract relations
EVALUATION
1. Evaluation in terms of internal evidence
2. Judgments in terms of external criteria
Exhibit 2.1: Bloom’s Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain
If
you recall the objective statements, you will find that there were two major
components
of an objective:
a)
Some subject matter content (A Noun or Noun phrase)
b) A
description of what is to be done with or to that content (A verb or verb
phrase)
For example, “a learner will be able to define motion.” In this objective
statement
the noun phrase is “motion” and the verb is “define.” In original
taxonomy,
noun and verb aspects was part of knowledge dimension.
In
the revised taxonomy, first change is that noun and verb dimensions are
separate.
The noun is providing the basis for the Knowledge dimension and the
verb
is forming the basis for the Cognitive Process dimension.
The Knowledge Dimension
The
new knowledge dimension contains four
categories i.e. factual,
conceptual,
procedural and metacognitive. Metacognitive
Knowledge involves knowledge
about
cognition in general as well as awareness of and knowledge about one’s
own
cognition.
A) FACTUAL KNOWLEDGE – The basic
elements that learners must
know
to be acquainted with a discipline or solve problems in it.
a) Knowledge
of terminology
b) Knowledge of specific details and elements
B) CONCEPTUAL KNOWLEDGE – The
interrelationships among the
basic
elements within a larger structure that enable them to function
together.
·
Knowledge of classifications and categories
·
Knowledge of principles and generalizations
·
Knowledge of theories, models, and structures
C) PROCEDURAL KNOWLEDGE – How to do
something; methods
of
inquiry, and criteria for using skills, algorithms, techniques, and
methods.
·
Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms
·
Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and
methods
·
Knowledge of criteria for determining when to
use appropriate
procedures
D) METACOGNITIVE KNOWLEDGE – Knowledge
of cognition in
general
as well as awareness and knowledge of one’s own cognition.
·
Strategic knowledge
·
Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including
appropriate contextual
·
and conditional knowledge
·
Self-knowledge
Exhibit 2.2: The Knowledge Dimension
The Cognitive Process Dimension
In
this dimension, like the original taxonomy, same number exists in the revised
taxonomy
also. Let us see the following table to understand the changes in revised
taxonomy.
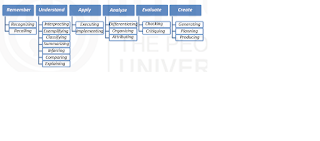
In attach table
, you can see that ‘knowledge’ category is renamed as ‘remember’,
‘comprehension’
is renamed as ‘understand’, ‘Application, Analysis and
Evaluation’
are retained but in their verb form i.e. ‘apply, analyze and evaluate’.
Evaluation
was last category in original taxonomy but here it is at 5th place and
‘synthesis’
is replaced by a new category named as ‘create’.
All
these 6 categories are further divided into 19 subcategories and renamed as
cognitive
processes. Let us have an overview of these cognitive processes

Comments
Post a Comment